Do you know About Complete Cat Anatomy?
Learn cat anatomy with this complete guide covering cat body parts, internal organs, skeleton, and muscles. Perfect for pet owners who want to understand how a cat’s body works and how anatomy affects health, behavior, and daily care.
Understanding cat anatomy is one of the most important things every cat owner should learn. Although cats may look simple on the outside, their bodies are actually complex, powerful, and perfectly designed for hunting, jumping, and surviving in different environments. From sharp senses to flexible bones, every part of a cat’s body has a specific purpose.
In this detailed guide, we will explore cat anatomy step by step. We’ll look at external body parts, internal organs, skeletal structure, muscles, and how everything works together. Whether you are a new cat owner or a lifelong cat lover, this guide will help you understand your feline companion better.
Why Understanding Cat Anatomy Is Important
First of all, knowing cat anatomy helps you recognize health problems early. For example, if you understand where a cat’s kidneys or stomach are located, you may notice unusual swelling or pain sooner. Additionally, it helps you communicate better with veterinarians and make informed decisions about your cat’s care.
Moreover, understanding how a cat’s body works improves daily care such as grooming, feeding, and exercise. As a result, your cat can live a longer, healthier, and happier life.
External Cat Anatomy: Visible Body Parts
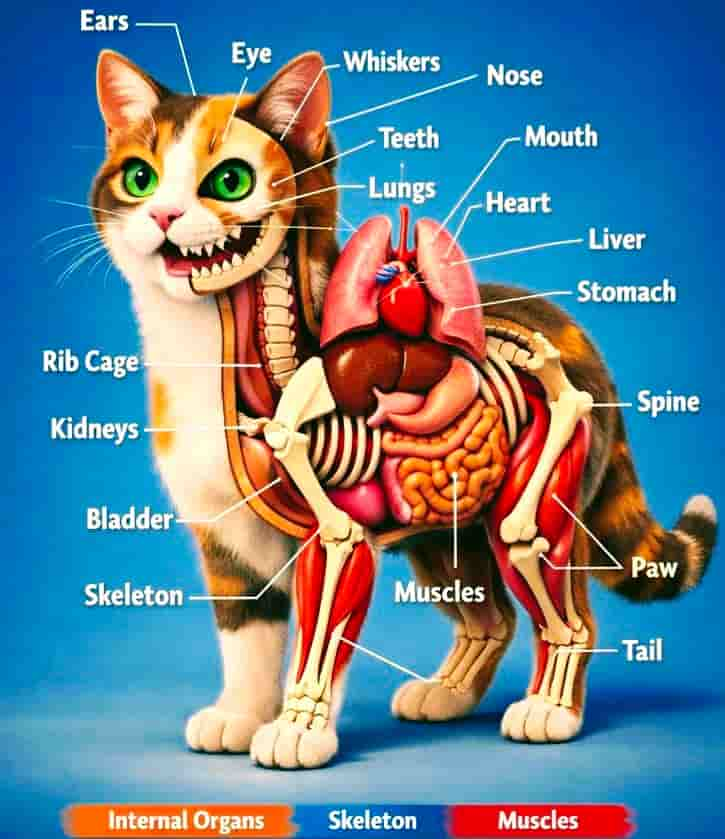
Let’s start with the parts of a cat’s body that we can see easily.
Head and Face Structure
A cat’s head is small but extremely efficient. It holds powerful sensory organs that help cats survive.
Eyes
Cats have large eyes compared to their head size. This allows them to see clearly in low light. Their eyes are designed for hunting, especially at dawn and dusk. Additionally, the reflective layer behind the eye helps improve night vision.
Ears
A cat’s ears are highly flexible and can rotate almost 180 degrees. This helps them detect even the smallest sounds. Because of this, cats can hear frequencies much higher than humans.
Whiskers
Whiskers are not just hair. They are sensitive tools that help cats judge space, balance, and movement. Whiskers are deeply rooted and connected to nerves, making them extremely sensitive.
Nose
A cat’s nose plays a major role in smell. Cats rely heavily on scent to identify food, people, and other animals. Each cat has a unique nose pattern, just like human fingerprints.
Mouth, Teeth, and Jaw Anatomy
The mouth is a vital part of cat anatomy, especially for eating and defense.
Teeth Structure
Cats have 30 permanent teeth. These teeth are sharp and designed for tearing meat, not chewing. This reflects their nature as obligate carnivores.
Tongue
A cat’s tongue is covered with tiny hook-like structures called papillae. These help with grooming and removing meat from bones.
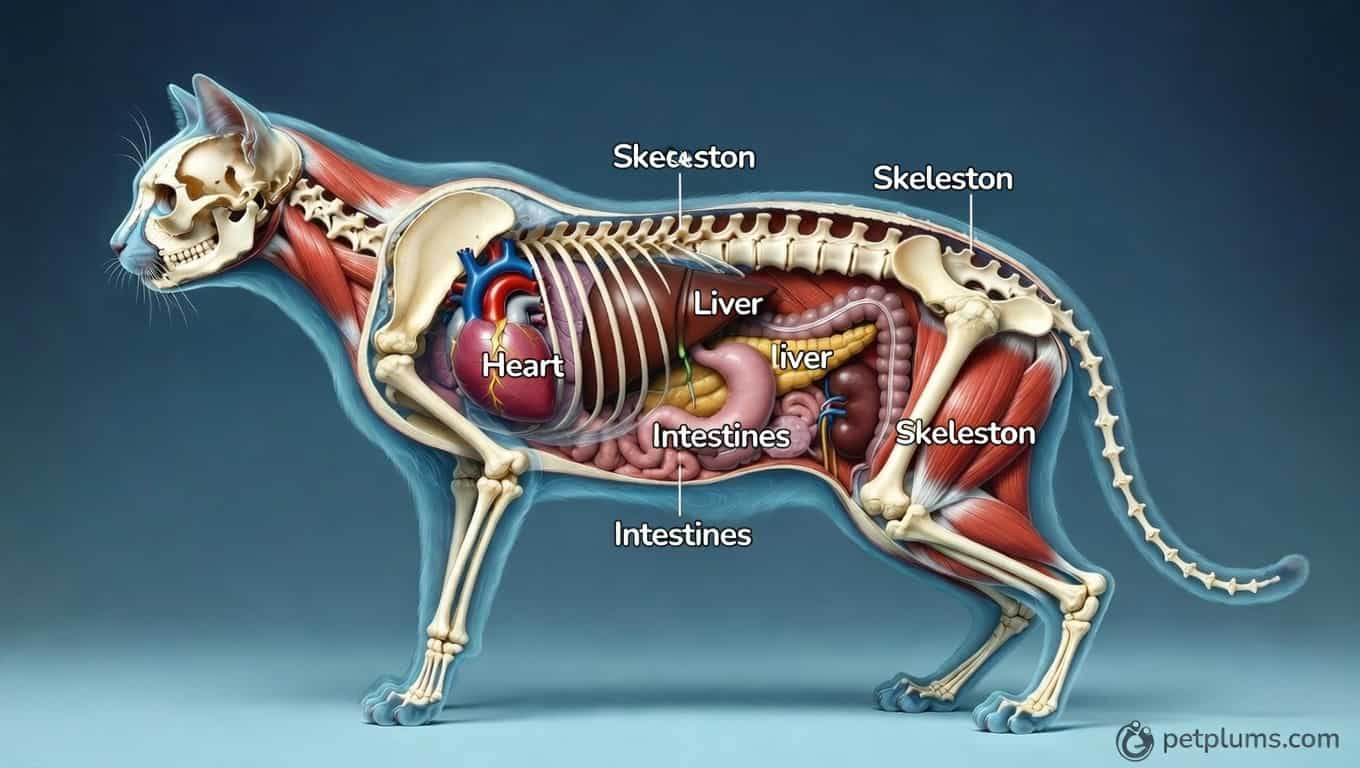
Cat Skeleton: Bone Structure Explained
The skeletal system is one of the most fascinating parts of cat anatomy.
Number of Bones
Cats have approximately 230 bones, which is more than humans. This extra bone count gives them flexibility and agility.
Spine and Flexibility
A cat’s spine is extremely flexible. This allows cats to twist their bodies mid-air and land on their feet. As a result, cats are excellent jumpers and climbers.
Rib Cage
The rib cage protects vital organs such as the heart and lungs. It is flexible enough to allow easy breathing but strong enough to protect internal organs.
Legs and Paws
Cats walk on their toes, a movement known as digitigrade walking. This helps them move quietly and quickly. Their paws also contain soft pads that absorb shock.
Muscular System: Power Behind Every Movement
Muscles play a major role in cat anatomy, allowing cats to jump up to six times their body length.
Muscle Groups
Cats have powerful muscles in their hind legs, shoulders, and back. These muscles work together to provide strength and speed.
Tail Muscles
The tail helps with balance and communication. Muscles in the tail allow precise movements that help cats stay stable while jumping or walking on narrow surfaces.
Internal Organs: Inside Cat Anatomy
Now let’s explore the internal organs that keep a cat alive.
Heart
A cat’s heart pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients. It beats faster than a human heart, which supports their active lifestyle.
Lungs
The lungs help cats breathe and supply oxygen to the blood. Healthy lungs are essential for energy and stamina.
Liver
The liver plays a critical role in digestion and detoxification. It helps break down fats and remove toxins from the blood.
Stomach and Digestive System
Cats have a simple digestive system designed for meat digestion. Their stomach produces strong acids to break down protein efficiently.
Kidneys
Kidneys filter waste from the blood and regulate hydration. Kidney health is extremely important because kidney disease is common in older cats.
Recommended External Link (Trusted & Relevant)
https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/pet-owners/petcare/your-cats-health
Nervous System and Brain
The brain controls movement, behavior, and instincts. Cats have a well-developed nervous system that allows quick reactions and excellent coordination.
Reproductive Anatomy (Brief Overview)
Male and female cats have different reproductive organs, designed for efficient reproduction. Understanding this part of cat anatomy is important for breeding and spaying or neutering decisions.
How Cat Anatomy Supports Natural Behavior
Everything in cat anatomy supports natural behaviors such as hunting, climbing, grooming, and playing. Their sharp senses, flexible spine, and strong muscles make them natural predators.
Common Cat Anatomy Myths
Many people believe myths such as cats having nine lives or always landing on their feet. While cats are agile, injuries can still occur if they fall from great heights.
How Cat Anatomy Changes With Age
Kittens, adult cats, and senior cats have different anatomical needs. As cats age, muscles may weaken, bones may stiffen, and organs may require special care.
Final Thoughts
Understanding cat anatomy helps you become a more responsible and caring pet owner. From external features like whiskers and paws to internal organs like the heart and kidneys, every part of a cat’s body works together in perfect harmony.
By learning how your cat’s body functions, you can improve their health, happiness, and overall quality of life.